Having a fast-loading website is essential in the online domain, where every website strives to be the top choice for their target audience. Implementing web caching techniques can be a game-changer in achieving this goal.
In this article, we’ll explain caching, why it is important for your website, and recommend some of its best practices.
What Is Caching?
Caching is the process of storage of certain assets on a local level to get used again for a full round trip request to the server.
All the information, such as HTML, JavaScript, CSS, and Images can be cached. These cached items come with an expiry label to inform the browser how long each item can be stored, re-used, or fetched freshly from the server.
If you want the Google bot to clearly understand what your website offers, then you should take a look at the Google cache of your website.
Google cache viewer is a way to observe how caching is. It offers a snapshot of your website by using the crawling bots and creates a backup in case the current page is unavailable. The last-visited website will be viewed and indexed to compare the changes.
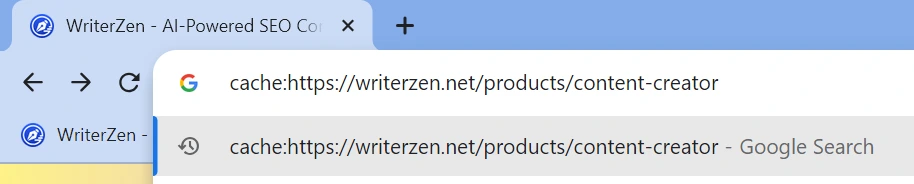
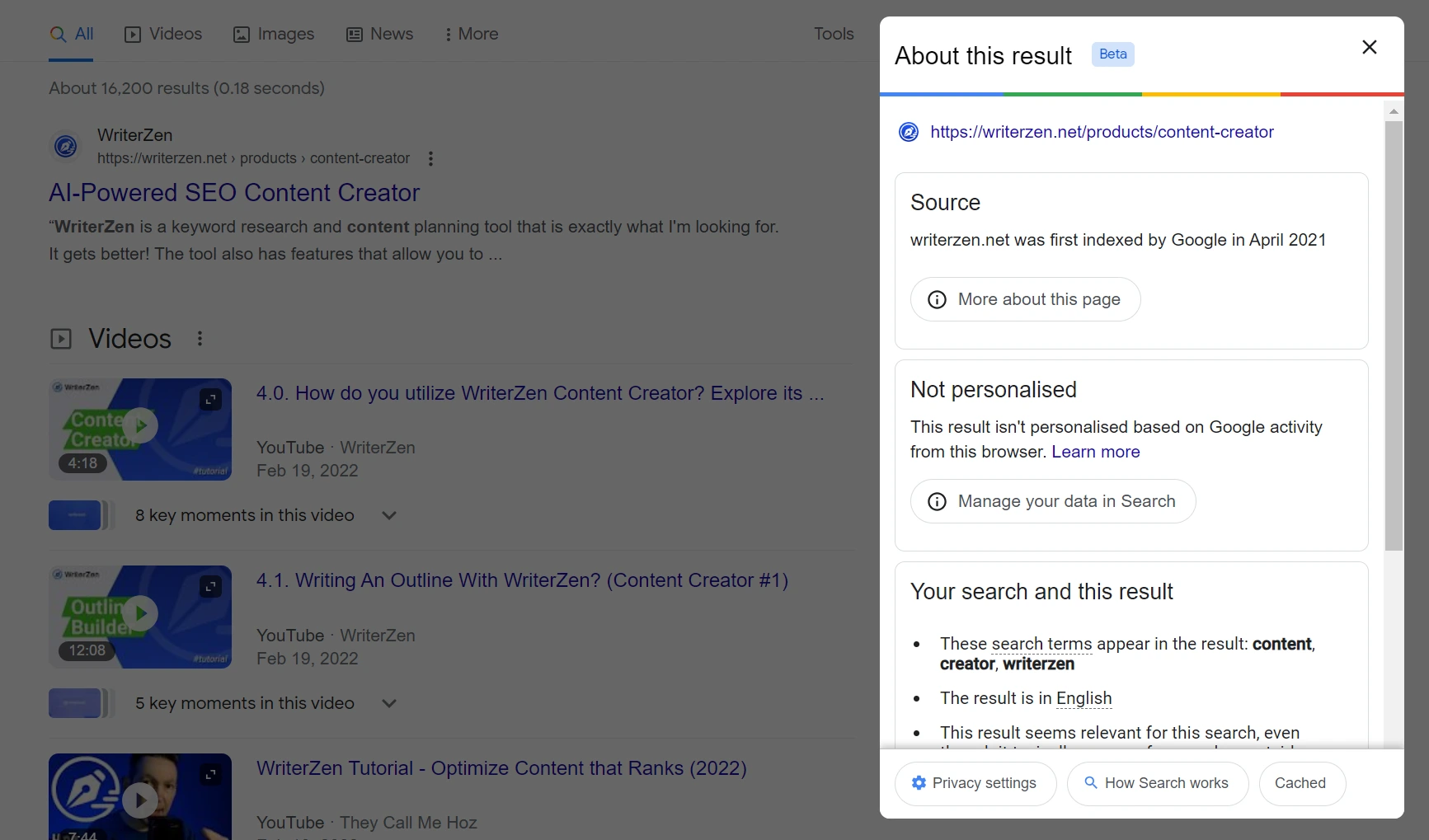
You can check out the latest cached version of any website by using the prefix “cache:” before the URL when using Google Chrome.
Or, you can click on the three vertical dots next to the URL on the SERP, leading you to the “About this result” section. Clicking on “Cached” will take you to the latest cached version of the website.
Why Is Caching Important for Your Website?
In case your website does not generate enough traffic or does not get crawled effectively by the Google bot, then you have come to the right place to learn to fix that.
Serve as a Valuable Backup
Marketers constantly make changes to their websites for improved performance and peak-quality user experience. In the event of a page being hacked or deleted, accessing the cache can serve as a valuable backup or memory that contains the necessary information in case the website is hacked or deleted.
Improve Loading Speed
An appropriate and standard caching setting speeds up loading time for your website’s visitors. Google recommends setting a caching lifetime of one year for static assets, but you can go even further by implementing strong version control practices.
This involves changing the file name from the server, prompting a request for the updated file instead of relying on the cached version. However, failing to set caching lifetimes can lead to issues such as fetching fresh cache and slowing down the loading time for each webpage.
Image and Visual Optimizing
Every cached website comes with a “text-only version” that shows how Google bots read the website.
Since the algorithm cannot read pictures but text, you must include readable elements like image alt tags so that the Google bots can recognize the image's content. Each of these visual elements needs to have info-rich content and a heading to make it relevant for Google.
Avoid loading the page with too many keywords. It alerts Google bot and flags your website as unhealthy and unfair in terms of SEO practices and spoils your rankings.
Enhance and Improve Website Content
Regularly updating your web pages with fresh content has a direct impact on how often Google crawls your site. The frequency and quality of your content updates contribute to improving your page's ranking.
When you consistently provide high-quality content, Google will index your site more frequently during its crawls.
Types of Caching

-
Web Caching: Data gets stored for getting used again. It is stored as a copy of the website from the web server. It is the first to get cached when a user visits the page for the first time.
-
Data Caching: It is the type of data in the cache that enables the computer to perform better and faster. It speeds up data retrieval which can take more than usual time.
-
Application or Output Caching: It stores the HTTP responses to the generated page output, and controls in the memory to enable you to cache various types of content based on the query string.
-
Distributed Caching: It is a type of cache that serves multiple app servers and is handled by an external service to app servers when they can access it.
Caching Best Practices
-
Integrate quickly with your application platform: You can optimize your application platform settings to help you directly integrate with your content management system.
-
Keep checking your cache hit ratio: Calculate the number of requests getting delivered by a cache server and divide it by the number of cacheable requests. This can be calculated as the number of hits and misses. This is called the cache hit ratio.
-
Set a default fallback TTL that can be updated anytime: TTL is based on cache-related header details that get returned from your origin server.
-
Configure quickly to briefly serve old content: If the origin becomes unavailable for an extended period for any maintenance or other reasons, you can serve old or stale content to amp up the site’s static content.
-
Handle custom errors: By creating custom error messages including specific information related to the request made and applicable to the user.
-
Always inform customer support: Timely provide them about the problems with details like the time, date, event type, period, and how the services are being affected.